What is Cement?
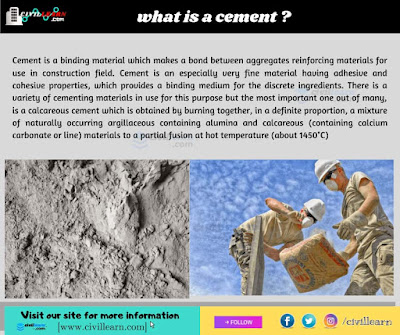
Cement is a very important material for use in the construction field because without cement↗ the construction work is not possible. It is an especially very fine material having adhesive and cohesive properties, which provides a binding medium for the discrete ingredients. There is a variety of cementing materials in use for this purpose but the most important one out of many, is a calcareous cement which is obtained by burning together, in a definite proportion, a mixture of naturally occurring argillaceous containing alumina and calcareous (containing calcium carbonate or line) materials to a partial fusion at hot temperature (about 1450°C)Main different types of cement and their uses (AS PER IS CODE)
Cement↗️ exhibit different properties and characteristics depending upon their chemical compositions. By changing the fineness of grinding or the oxide composition, cement can be made to exhibit different properties. The use of additives, different raw materials and changing the chemical composition has resulted in the availability of many types of cement to cater to the need of the construction industry for specific uses and purposes according to work.
The different types of cement are the following given below.
1. Ordinary Portland cement (OPC)
2. Rapid hardening cement
3. Sulphate resisting cement
4. Air-entraining cement
5. Coloured cement
6. High alumina cement
7. Blast furnace slag cement
8. Low heat cement portland cement
9. Portland pozzolana cement (PPC)
10. Oil well cement
11. Hydrophobic cement
12. Quick setting time cement
13. Expensive cement 14. White cement
15. Waterproof portland cement
1. Ordinary Portland cement (OPC)
This type of cement is so far the most important type of cement. Approximately about 60% of the cement used in the country is ordinary Portland cement prior to 1987, there use to be only one grade of OPC which was governed by IS:269-1976. after 1987 higher grades of cement were introduced in India and were classified as 33 grade, 43 grade, and 53 grade. This classification was dependent upon the strength, achieved by cement, after 28 days of curing. The strength value may be higher than 43 N/mm2 (MPA).Type of portland cement has also a medium rate of strength development and warmth generation. As per BIS (Bureau of Indian Standards) classification of cement has been graded into three categories.
It has been possible to upgrade the qualities of cement by using high-quality limestone, modern equipment, closer on constituents control, maintaining better practice size distribution, finer grinding and packing. The manufacture of OPC is decreasing all over the word in view of the popularity of blended cement on account of lower energy consumption, environmental pollution, better quality, and high performance. This type of cement is widely used in all type of construction work.
Properties - Following are the properties of ordinary Portland cement
- When sieved through IS sieve No. 9, then reduce the residue should not exceed 10% by weight.
- The initial setting time is not less than 30 minutes and the final setting time not more than 10 hours.
- When resists for soundness, the expansion shall not be more than 10mm.
2. Rapid hardening cement
The cement is much similar to ordinary Portland cement. As the name indicates, it develops strength rapidly than normal cement. Therefore, sometimes, it may also be called as high early strength cement. It may be noted that rapid hardening cement, which develops strength at a higher rate may not be confused with quick setting time, which sets very quickly.
The strength of rapid hardening cement at 3 days is equal to 7 days strength of OPC with a similar water-cement ratio. The rapid rate of development of strength is attributed to the higher fineness or grinding (with a specific area not less than 3250 sq. Cm per gram), higher content of C3S and lower content of C2S content also results in faster hydration. Rapid hardening cement results in higher heat of hydration during the early period and hence should not be used in mass concreting.
Properties - Following are the properties of rapid hardening cement
- When sieved through IS sieved no. 9, the residue should not exceed 5% by weight.
- Initial setting time should not be less than 30 minutes and the final setting time should not exceed 10 hours.
- When tested for soundness, the expansion should not be more than 10 hours.
- After 1 day the compressive strength will not be less than 16(N/mm2).
- After 3 days the compressive strength will not be less than 27(N/mm2).
Uses - Following are the uses of rapid hardening cement
- It used when high early strength is required e.g. when it is required to remove the formworks early and reuse elsewhere.
- In precast concrete work.
- Repair of road and airfields, where it is important to open the traffic without delay.
- It is helpful in cold weather concrete, where the rapid rate of development of strength protects concrete against freezing and reduce the vulnerability of concrete to the frost damage.
3. Sulphate resisting cement
Ordinary Portland cement is susceptible to the attack of sulphate e.g., magnesium sulphate. Solid sulphate does not attack the cement compound but sulphate in solution permeate into hardened concrete and attack, calcium aluminate and hydrated silicates. This is known as sulphate attack which may result in cracks and subsequent disruption. Sulphate attack is generally accelerated if accompanied by alternate wetting and drying which mostly occur in marine structures.To provide remedy resistant against sulphate attack, the use of cement with low C3A content is found to be effective. Such cement with low C3A and relatively low C4AF content is known as sulphate resisting cement. Due to this low combination of compounds, cement has high strength but the early strength is low. The compressive strength when standard sand is used shall not be less than after 3 days 15(N/mm2), after 7 days 22 (N/mm2) and after 28 days (30N/mm2).
Properties - Following the properties of sulphate resisting cement
- When sieved through IS sieved no. 9, the residue must not exceed 5%.
- The initial setting time is not less than 30 minute and final setting time not more than 10 hours.
- The compressive strength is as mentioned below.
Uses - Following are the uses of sulphate resisting cement
- It's also used for the development of the concrete structure in matric condition.
- It's also used for structures which are likely to be damaged by severe alkaline conditions like culverts, canal lining, the underside of railway bridges, etc.
- It's used for the construction of the foundation where the soil is rich in sulphate.
- It's also utilized in the development of sewage treatment works.
- This type of cement is mostly used in construct pile foundation.
4. Air-entraining cement
Air-entraining cement is not covered under India standards so far. This cement is manufactured by mixing a small amount of air-entraining agents with ordinary Portland cement during the process of grinding. The following types of air-entraining agents could be used.- Wood resins like vinsol resin.
- Synthetic detergents of the alkyl-aryl sulphonate type.
- Calcium salts of glues and other protein obtained in the treatment of animal hides.
The air-entraining agents are added in powder or liquid forms to the extent of 0.025 to 0.1% by weight of cement clinkers. Use of air-entraining cement produces minute (0.075mm to 1.25mm in diameter) and well-distributed air bubbles in the body of concrete which will modify the properties of plastic concrete to workability, segregation and bleeding. The main purpose has used this type of cement is to fill up the gap in the concrete which are produced by the excessive amount of water during casting it is especially helpful for increase the workability with few water-cement ratios.
Uses - Following are the uses of Air-entraining cement
- It is helpful in making the concrete walls and roofs for sound and heat insulation properties.
- It is helpful in making the concrete free from bleeding and segregation.
- It id used to get better workability with low water-cement ratios.
5. Coloured cement
The ordinary Portland cement is greyish in the colour due to the presence of iron oxide. For manufacturing different coloured types of cement either white cement or grey portland cement is used as a base.
- The cobalt gives a blue colour.
- The chromium oxide gives a green colour.
- The Manganese oxide gives mainly black or brown coloured cement.
- Iron oxide in different properties gives brown, red or yellow colour.
Coloured cement consists of portland cement with 5 - 10% of different coloured pigments. For uniform mixing of pigment, it is necessary to grind the pigment and cement together. The desired properties of colouring pigments are. the durability of colour, absence of solute salts, the fine state of division, not affected by cement.
Uses - Following are the uses of coloured cement
- This type of cement is basically very useful for decorative works such as floor finish, face works etc.
- This type of cement is also used for ornamental construction work.
Also read
- Introduction of Concrete | Main Classification, their Properties and advantages↗️
- [7] Main Test of cement | Explain types of Field and laboratory test of cement↗️
6. High alumina cement
This type of cement is obtained by fusing a mixture of alumina and calcareous materials, in suitable proportion, and grinding the resultant product to a fine powder. The ingredients used for the manufacturing of high alumina cement are limestone and bauxite (A12O32H2O). bauxite is an aluminium ore. This cement has higher impermeability and is used for special works. the initial setting time should not be less than 30 minutes and the final setting time is not more than 10 hours. When tested for soundness, the expansion should not exceed 5mm. The compressive strength when standard sand is used shall not be less than after 1 day 30(N/mm2) and after 3 days 35 (N/mm2).Uses - Following are the uses of High alumina cement
- This is suitable for colder regions because of its advantages of high early strength and heat of hydration.
- It is used in underwater construction and manufacturing of thin sections like electric poles, piles, road, slabs etc.
7. Blast furnace slag cement
The waste product obtained in the manufacturing of pig iron is known as blast furnace slag cement the portland cement obtained by mixing portland cement clickers, gypsum and granulated blast furnace slag in suitable proportion and grinding the mixture to obtain a thorough and intimate mixture between the ingredients is called blast furnace cement.It has similar properties as that of (OPC) cement and therefore can be used in all places. It has low early days strength and hence, it requires a long curing period. The cost of blast furnace slag cement is less as compared to ordinary Portland cement. It generated less heat of hydration. The initial setting time should not be less than 30 minutes and the final setting time should not be more than 10 hours. The soundness test value should not be more than 10mm. The compressive strength when standard sand is used will not be less than after 3 days 16(N/mm2) and after 7 days 22(N/mm2).
Uses - following are the uses of Blast furnace slag cement
- It is more resistance to sulphate attack, therefore, it can be used for marine works or cement pipes carrying chemicals
- Dew to low heat of hydration, it is suitable for mass concrete works such as dams, retaining walls, etc.
- It can be used for all construction works where ordinary Portland cement can be used.
8. Low heat cement
The name has generally denoted this type of cement generate a lesser amount of heat of hydration. Low heat evolution is achieved by reducing the contents of C3S and C3A which are the compounds evolving the maximum heat of hydration. The rate of evolution of heat will be less and the evolution of heat will be less and the evolution of heat will extend over a longer period. The main feature of the low heat cement is the slow rate of gain of strength but the ultimate strength is the same as that of ordinary Portland cement. The initial setting time should not be less than 30 minutes and the final setting time should not be more than 10 hours. The soundness test value should not be more than 10mm. The compressive strength when standard sand is used will not be less than after 3 days 10(N/mm2), after 7 days 16(N/mm2) and after 28 days 35(N/mm2).
Uses - following are the uses of Low heat cement
- It is helpful to resist moderate sulphate attack.
- It used only in large mass concrete works like dams, retaining wall, bridge abutments, etc. changes of cracks are reduced.
9. Portland pozzolana cement (PPC)
The pozzolanic materials generally used for the manufacture of PCC are fly ash or calcined clay. Fly ash is a waste material, generated in the thermal power station when powdered coal is used where ordinary portland pozzolana cement be used where ordinary Portland cement is usable. When sieved through IS sieved no. 9, the residue shall not exceed 5% by weight. The initial setting time is not less than 30 minutes and the final setting time is not more than 10 hours. The main purpose of using this type of cement is very cheap rather than another type of cement.
Advantages of PPC
- It has a high resistance to chemical attacks.
- PCC being finer than OPC and hence reduces permeability.
- It generates reduced heat of hydration and that too at a low rate.
- In PPC, costly clinker is replaced by cheaper pozzolanic materials and hence economical.
Disadvantages of PPC
- The rate is of strength slower than OPC.
- Reduction of alkalinity reduces the resistance to corrosion of steel reinforcement.
Uses - Following are the uses of Portland pozzolana cement
- It is used in the construction of hydraulic structures and mass concrete structures, such as dams, weirs, etc. Because to improve the permeability of concrete.
- It is used for sewers and sewage disposal works etc.
- PCC can be used in all situations where OPC is used except where high early strength is required.
10. oil-well cement
The cement is mainly used for sealing the sides of wells so that the slide of the freshly drilled well from collapsing can be prevented. The cement slurry has to be pumped into position at a high temperature of 175℃ and high pressure of 1300 kg/cm². this cement slurry is used to seal off the annular space between steel casing and rock strata. This type of cement should have quick hardening and slow setting properties can be obtained in two ways.- By adding retarders to OPC
- By adjusting the compound composition of the cement I.e., to have very little C3A.
11. Hydrophobic cement
This is which is clearly defined from the name, Hydro means water and phobic is generally means is against. It is produced from by mixing water-repelling chemicals and has high workability and strength has the property of repelling water and it is unaffected during wet climates such as monsoon or rains. This type of cement is mainly used for the construction of water structures such as dams, water tanks, spillways, water retaining structures and other types of structure.The strength of this cement is the same as that of ordinary portland cement after 28 days. This is generated by grinding portland cement clinker and with a film-forming substance such as oleic acid in order to decrease the rate of deterioration when the cement is stored under unfavourable conditions. These chemicals form a layer on the cement particle and do not allow water to mix and start the hydration process in the transportation or storage stage. At during mixing process, due to great agitation, this layer of water repellent break and allows the hydration to take place.
The initial setting time of this cement should not be less than 30 minutes and the final setting time should not be more than 10 hours. The soundness test value should not be more than 10mm. The compressive strength when standard sand is used will not be less than after 3 days 16(N/mm2), after 7 days 22(N/mm2) and after 28 days 30(N/mm2).
Uses - Following are the uses of Portland pozzolana cement
- Hudge used in the Tunnel construction as the underground repairs are difficult and costly.
- Used in drainage system works and manholes septic tanks etc,.
- It's more useful for water treatment plants, dams and retaining walls.
- It can properly fix the leakage of pipes and basements.
12. Quick-setting cement
The name of the cement has clearly defined this cement is sett very quickly with comfortably another type of cement the main reason is it contains less gypsum and is finer than OPC. the initial setting time starts within 5 minute and final setting takes place within 30 minutes. This type of cement sets very early. Less amount of gypsum and fine grinding is responsible for accelerating the starting action of cement.It mostly used in underwater construction where pumping is involved. It may also find its use in some type of grouting operation.
13. Expensive cement
This is clearly defined from the name this type of cement is manufactured by adding stabilizer which stabilizes the cement to expand slightly with the time and doesn’t show any volume change after hardening such as plastic stage to a harder stage. It can be achieved by adding 8-20% of sulphoaluminate & 15% of stabilizer to the ordinary Portland cement clinker.
Concrete↗️ made up of OPC shrinks while setting due to loss of free water. Concrete also shrinks continuously for a long time. Cement used for grouting should not shrink or change the volume for this cement. This cement is mainly used for special work such as grouting anchor bolts and prestressed concrete ducts and another this type of work.
14. White cement
This type of cement which is clearly defined from the name this type of cement is mainly white in colour with the presence of a white base. It is mainly manufactured from the pure white chalk (CaCO3) and fine clay free from iron oxide.
The process of manufacturing of white cement is almost the same as (OPC) cement. The raw materials, particularly the kind of limestone (96%CaCO3) required for manufacturing white cement is available around Jodhpur in Rajasthan. Two famous brands available in the market are Birla white and J.K. white cement the properties of white cement is nearly the same as OPC cement. white cement is finer than grey cement. But it is not so strong as OPC cement. The initial setting time should not be less than 30 minute and final setting time is 10 hour. the soundness value should not greater than 10mm.
Uses - Following are the uses of coloured cement
- This type of cement is basically very useful for decorative works such as floor finish, face works, pointing etc.
- This type of cement is also used for wall putty.
- It is also used for interior work in the home.
15. Waterproof portland cement
This type of cement is manufactured by adding small percentages of metal creates in OPC during grinding. This is generated by grinding portland cement clinker and with a film-forming substance such as oleic acid in order to decrease the rate of deterioration This type of cement is used in foundations, water tanks & other water retaining structures. It is produced from by mixing water-repelling chemicals and has high workability and strength has the property of repelling water and it is unaffected during wet climates such as monsoon or rains. this type of cement is mainly used for special work.
Watch this video





![[3] Main method of estimation | Center line method and Long Wall-short Wall method](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEi-tUtY1W3S747Ws8mkCIvT9rCeji2iB5dIgISp1Y3SnuuLT3kcHKc6pm-eTghLLCoPSATf4L_dBVMvDCcstWv99RZc6ddp4yVoWT2mthaDW-1569tju756sMH3c3gDJZ_6iMkGcbd7c5U/w680/estimation+of+building.jpg)



0 Comments
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box.